R&D
Science
Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder, affectingmotor and non-motor functions of the central and peripheral nervous systems, including the dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra.The incidence of PD is one of the highest among all neurological disorders. PD is expected to affect 17 million people by 2040.PD is a progressive disorder, with few visible symptoms at onset. Gradual damage to the neurons translates into changes in behavior. Non-motor symptoms, such as loss of smell, constipation, and sleeping disorders, emerge long before the onset of the motor symptoms.The major motor symptoms of PD includeinvoluntary tremorsduring resting state, slow movement, and limb rigidity.
Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms

MOTOR
Tremor
Slowness of movement
Muscle stiffness
PSYCHOLOGICAL
Depression Anxiety
Cognitive impairment
Dementia
Psychosis
PHYSICAL
Balance problems
Loss of smell
Nerve pain
Problems with peeing
Constipation
Dizziness or fainting
Excessive sweating
Swallowing difficulties
Excessive production of saliva
Sleep problems
Weight loss
Current treatment and limitations
Most PD medications currently available relieve motor symptoms, compensatingfor the loss of dopaminergic neurons. These drugs do notprevent neuronal death or disease progression, and thus, after several years of administration,they require the use of higher dosages and are accompanied with unwanted side effects.
| Medication | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOA (Mode of action) |
Dopamine precursor | Dopamine agonist | Dopamine degradation inhibitors | Anticholinergics | |
| MAO B inhibitors | Cathecho O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitors |
||||
| API (Active pharmaceutical ingredient) |
Carbidopa-Levodopa | Pramipexole Ropinirole Rotigotine Apomorphine |
Selegiline Rasagiline Safinamide |
Entacoapone Opcapone Tolcapone |
Benztropine Trihexyphenidyl |
| Merits | Symptom relief | Prescribed with dopamine precursors | Control of tremor | ||
| Demerits | Side effects Drug resistance |
Side effects | Side effects | ||
PD pathology
Themain pathological traitsof PD are as follows:(1) selective loss of certain neurons, such as the dopaminergic neurons that project from the substantia nigrapars compacta, (2) neuroinflammation with microglialactivation, and (3) abnormal deposition of specific proteins in the forms of Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites.
Lewy bodies are mainlycomposed of alpha-synuclein.Oligomeric and fibrillar structures of alpha-synucleinmay promoteneuroinflammation and neuronal death. Alpha-synuclein aggregates initially occur in a few discrete regions of the brain and gradually spread to wider brain areas. The current theory is that this spread causes widespread neuroinflammation and neuronal loss, thereby promoting disease progression. The main strategy of Neuramedy is to develop disease-modifying drugs to halt the spread of alpha-synuclein.
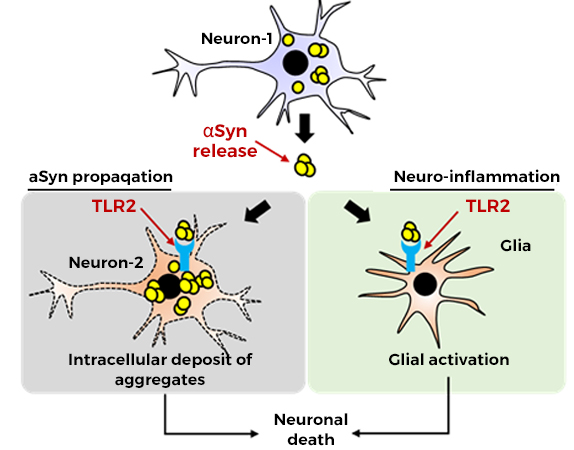
Alpha-synuclein and Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) in PD
Alpha-synuclein is a presynaptic proteinthat regulates synaptic transmission.It is an intrinsically disordered “flexible” protein. However, during aggregation, it is stacked together to form a structure rich in beta-sheet. Under abnormal conditions, alpha-synuclein aggregates are released from neuronsand can reach neighboring neurons, affecting their function and viability.
Neuron-derived alpha-synuclein also reacts with TLR2 on neighboring glial cells,resulting in inflammation ofthe brain parenchyma. Activation of the microglia and astroglia majorly contributesto PD progression. TLR2 also mediates neuron-to-neuron propagation of alpha-synuclein.
Because TLR2 is crucial to the propagationof alpha-synuclein and the resulting neuroinflammation, antagonizing TLR2 function is a promising strategy for blocking disease progression.
Neuramedy’s approach
Neuramedy aims to block the action of extracellular alpha-synuclein by the following approaches:
1) Blocking TLR2 to prevent the neuron-to-neuron propagation of alpha-synucleinand neuroinflammation
2) Inhibiting abnormal aggregation of alpha-synuclein and clearance of aggregates.
Our current projects arebased on the above principles.